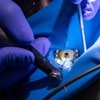
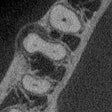
As a practicing endodontist, Friday evenings are always unpredictable. Patients in pain or referring dentists who are trying to help their patients in pain right before the weekend have become a norm in my practice.
 Dr. Deepika Ganne.AustinEndo
Dr. Deepika Ganne.AustinEndo
Identifying actual dental emergencies and referring them to the right specialist helps the patient immensely in getting the right kind of help, especially when time is of the essence. Pulp testing is essential in diagnosing an endodontic abscess from a periodontal abscess.
Endodontic emergencies can be classified mainly as the following:
- Symptomatic irreversible pulpitis with normal apical tissues
- Symptomatic irreversible pulpitis with symptomatic apical periodontitis
- Necrotic pulp with symptomatic apical periodontitis
- Necrotic pulp with fluctuant intraoral swelling (acute apical abscess)
- Necrotic pulp with diffuse facial swelling or cellulitis
Symptomatic irreversible pulpitis with normal apical tissues
This emergency presents as vital teeth that react with prolonged episodes of pain on exposure to mostly very cold or very hot temperatures. Pain persists even after the stimulus is removed.
Fractures, deep decay, or large restorations are mostly seen in these teeth. All sources of infection, like caries and defective restorations, should be removed completely.
Pulpotomy/pulpotomy with eventual completion of endodontic treatment is most helpful. Post-treatment anti-inflammatory medications (ibuprofen and acetaminophen) are sufficient. No antibiotics are necessary.
Symptomatic irreversible pulpitis with symptomatic apical periodontitis
These teeth are similar in characteristics to the above-described diagnosis. Vital teeth with pain on percussion are the marked difference.
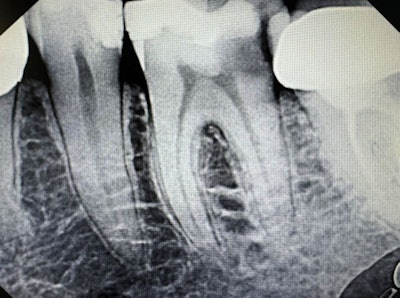 Symptomatic irreversible pulpitis with symptomatic periapical periodontitis.Dr. Deepika Ganne.
Symptomatic irreversible pulpitis with symptomatic periapical periodontitis.Dr. Deepika Ganne.
Complete pulp tissue removal and total debridement of the root canal are recommended with occlusal bite reduction. If root canal therapy cannot be completed due to time constraints, then placement of intracanal medicaments such as calcium hydroxide helps reduce the chances of bacterial growth in between appointments.
Anti-inflammatory medications are recommended. No antibiotics need to be prescribed.
Necrotic pulp with symptomatic apical periodontitis
Non-vital teeth with pain on percussion should be treated with a complete pulpectomy. Care should be taken to prevent apical extrusion of the debris to minimize post-op pain. Completion of the endodontic treatment in one or two visits is generally done. Calcium hydroxide is the intracanal medication used in between visits.
Leaving the tooth open to drain is not recommended. Apex locaters, cone-beam computed tomography imaging, and negative pressure irrigation systems (sodium hypochlorite, EDTA [ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid]) all help ensure optimum results.
Anti-inflammatory medications are recommended. Antibiotics can be prescribed on a case-by-case basis.
Necrotic pulp with fluctuant intraoral swelling (acute apical abscess)
Tissue swelling can be associated with acute apical abscesses at the initial dental visit or as a flare-up in between appointments. Swelling can be localized or diffuse, firm or fluctuant. Complete root canal debridement is essential in necrotic teeth with intraoral localized swelling, especially when the swelling is firm.
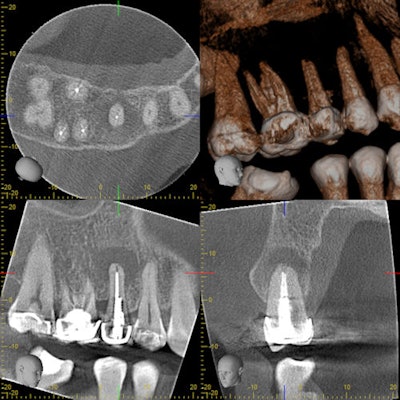 The CBCT indicates an acute apical abscess on a prior endodontically treated tooth.Dr. Deepika Ganne.
The CBCT indicates an acute apical abscess on a prior endodontically treated tooth.Dr. Deepika Ganne.
Incision and drainage help when fluctuant swelling is seen. Root canal therapy in two visits with calcium hydroxide as intracanal medicament is preferred. Anti-inflammatory medications and antibiotics are prescribed.
Necrotic pulp with diffuse facial swelling or cellulitis
Diffuse swelling is more extensive and can spread through adjacent soft tissues and fascial planes. When endodontic treatment is possible in such cases, complete root canal debridement is recommended.
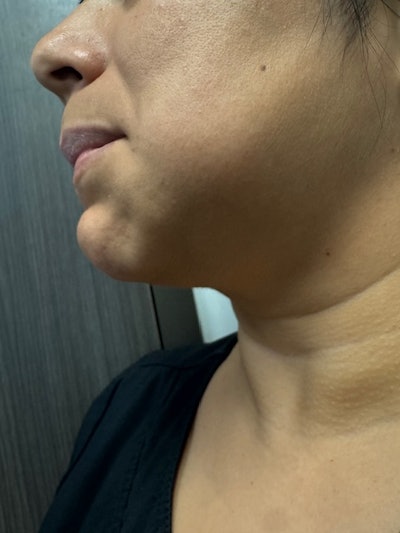 A patient presents with an abscess.Dr. Deepika Ganne.
A patient presents with an abscess.Dr. Deepika Ganne.
If the swelling is fluctuant, incision and drainage should be done with a rubber dam drain or Penrose drain placed for a day or two. Follow up with the patient daily for a few days. Analgesics and antibiotics are recommended.
If extraoral drainage is indicated, please refer the patient to an oral surgeon or the emergency room for follow-up and care. Teeth with prior root canals, trauma, or fractures can be included in the above classifications.
Please keep in mind that overuse of antibiotics has led to the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains of bacteria. When prescribing antibiotics, I recommend the patient take over-the-counter probiotics as well.
Steroids can be prescribed judiciously for severe pain to control inflammation. Correct diagnosis, definitive dental treatment, and pharmacologic management of pain and swelling are essential in managing endodontic emergencies.
Dr. Deepika Ganne is with Austin Endodontics in Austin, TX, where she currently serves as a practicing endodontist and owner-doctor at two locations: Cedar Park and Westlake. She is an active member of several professional organizations, including the American Association of Endodontists, the ADA, the Texas Dental Association, the Capital Area Dental Society, and she is a founding member of the Austin Indian Dental Association.
The comments and observations expressed herein do not necessarily reflect the opinions of DrBicuspid.com, nor should they be construed as an endorsement or admonishment of any particular idea, vendor, or organization.