A new dental implant surgical method that includes the use of a single drill and a bone-shaping instrument reduced bleeding and procedure time in a patient with coagulopathy. The case report was published on August 26 in the Journal of Prosthodontics.
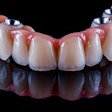
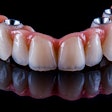
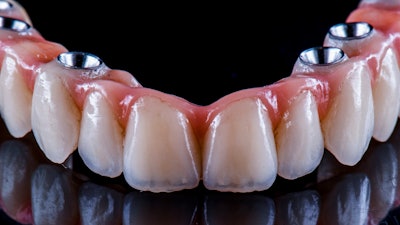
In addition to the unique technique, new trioval implants were loaded immediately and used to support a complete arch fixed implant-supported zirconia prosthesis. The success of this case suggests that the technique may be a good option for other patients who require swift management and shorter intraoperative treatment times due to dental phobia or other health conditions, the authors wrote.
“A novel site preparation protocol using a novel implant offered a significant advantage in the management of this patient who had a significant medical history and coagulopathy issues,” wrote co-author Dr. Mikhail Babayan of the division of prosthodontics at the University of Connecticut Health Center in Farmington.
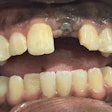
A 68-year-old edentulous man
The subject of the case study -- a man who had numerous health conditions, including atrial fibrillation, hypertension, and myocardial infarction -- visited a prosthodontist to improve his aesthetics and masticatory efficiency. To manage his conditions, he was taking antihypertensives, proton pump inhibitors, antihistamines, antacids, alpha blockers, and omega-3 fatty acids. His oral anticoagulants included a daily dose of 5 mg of apaxiban and 81 mg of aspirin. Also, the man had recently been admitted to the hospital after undergoing a full-mouth extraction due to a sublingual hematoma, according to the report.
After an exam and imaging, it was agreed that he be fitted with six mandibular and six maxillary implants to support a zirconia complete arch fixed implant-supported prosthesis. Following discussions with the patient’s other medical providers, it was recommended that the man discontinue blood thinners for three days before the surgery, the number of local anesthetics containing epinephrine be limited, and treatment time be minimized, the authors wrote.
Both the patient and his medical team selected the novel implant system and technique, which includes a significantly shortened drilling protocol and use of an osseoshaper, a new implant-specific bone-shaping instrument. The patient selected it because it saved him extra costs associated with procedures completed in a hospital, and the medical team favored it because it was simpler and more convenient for the patient.
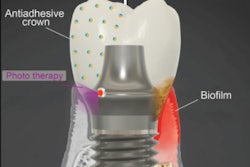
Unlike conventional osteotomy preparation protocol, the new method doesn’t use sequential drills at varying speeds to expand the site. Instead, the new protocol involves the use of a single drill and the osseoshaper followed by placement of the implant with a novel trioval connection, they wrote.
Also, the process of osseoshaping is unique compared to the screw tap used in traditional implant surgeries. The silhouette of the osseoshaper and its rake angles, as well as its method of expanding the bone from the initial diameter of the first drill to the final diameter of the planned implant, are distinct, the authors wrote.
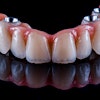
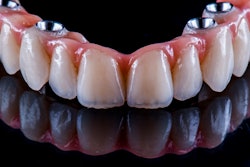
The patient underwent implant surgery without any postoperative bleeding or hematoma formation, and all implants survived with excellent bone levels. After healing, the zirconia prostheses were inserted successfully. The man was pleased with his treatment, they wrote.
Mitigating risks, adding benefits
Bleeding disorders that prevent a person’s blood from clotting, as well as the use of oral anticoagulants and some dietary supplements, are complications to dental surgery. Typically, the methods of managing bleeding during implant surgeries often include discontinuing anticoagulant use, applying compression, and using local anesthesia containing vasoconstrictors, the authors wrote.
Management strategies can require that some surgeries be performed in hospital settings, which are more expensive. Also, there are advantages to performing implant surgery more quickly and efficiently, including decreased overall treatment time and complications and greater patient satisfaction.
“Aside from conventional management techniques for coagulopathy, this case report offers an additional approach to reduce intra-operative treatment time without compromising on any clinical outcomes,” Babayan and colleague wrote.